Therapies
Built on 20+ years of advancing critical care delivery, the PRISMAFLEX and PRISMAX Systems are designed to allow easy implementation of multiple modality options and therapies.
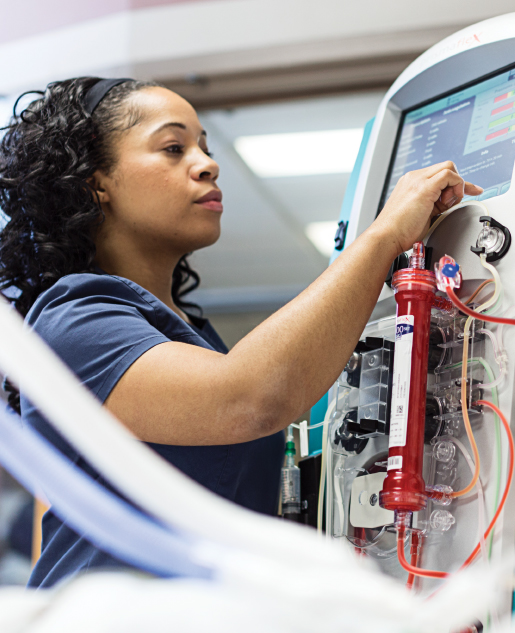

Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
Designed with safety and ease of use in mind. PRISMAFLEX and PRISMAX Systems’ intuitive interface provides step-by-step user-guidance, and allows the flexibility to easily switch between four treatment modalities.
Additionally, the scale-based system provides accurate real-time measurement to help ensure a clear understanding of patient status and treatment parameters.
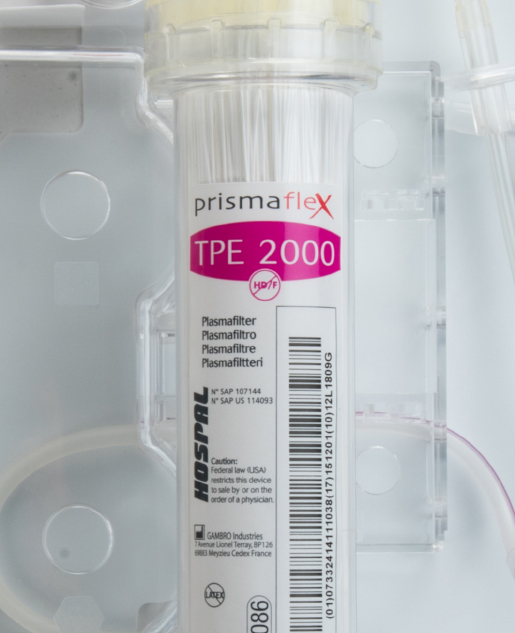
Therapeutic Plasma Exchange
Hospitals that own PRISMAFLEX or PRISMAX Systems can run membrane TPE without purchasing an additional machine. The disposable TPE 2000 Set is the only extra part needed to run this therapy on a PRISMAX or PRISMAFLEX System.
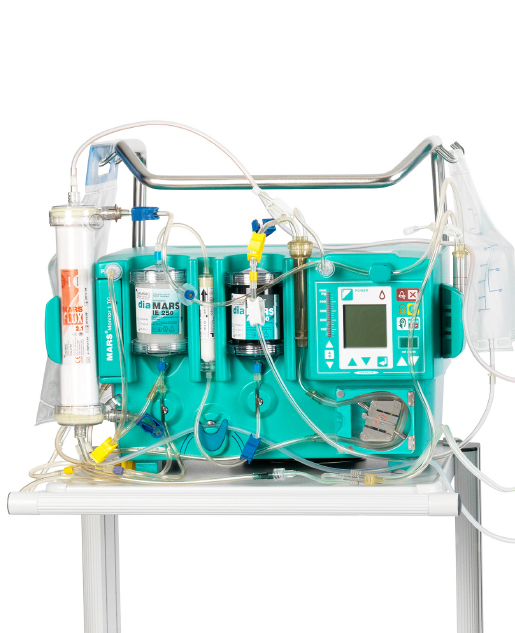
Liver Detoxification
MARS (Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System) works with the PRISMAFLEX System* to provide support for the removal of harmful drugs and poisons in combination with CRRT. The MARS therapy is indicated for the treatment of drug overdose and poisoning. The only requirement is that the drug or chemical be dialyzable (in unbound form) and bound by charcoal and/or ion exchange resins.
*MARS currently available in the US for PRISMAFLEX System only.
|
The PRISMAFLEX and PRISMAX Systems are intended for: PHOXILLUM and PRISMASOL Renal Replacement Solution Indications and Important Risk Information Indications and Usage
|
|
Please see PHOXILLUM and PRISMASOL Solutions full Prescribing Information. MARS is indicated for the treatment of drug overdose and poisonings. The only requirement is that the drug or chemical be dialyzable (in unbound form) and bound by charcoal and/or ion exchange resins. |